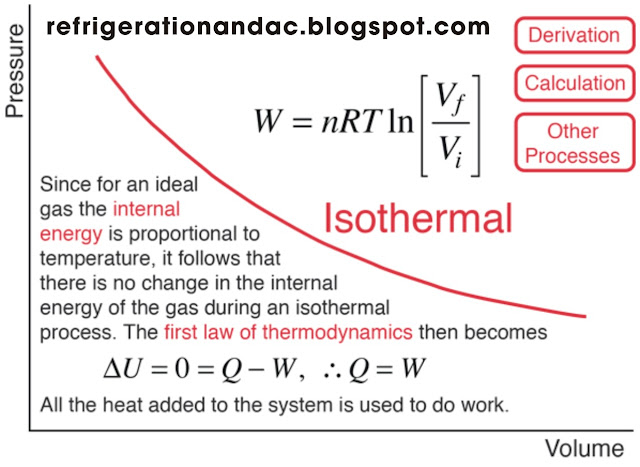
An isothermal condition is the expansion or contraction of a gas which occurs without a change in temperature (Boyle's Law, Par. 1-50). This condition can occur either during the expansion or the compression of a gas.
During the expansion of a gas, the gas is cooled and therefore the heat necessary to keep the gas at a constant temperature must be obtained from an outside source. The heat obtained from the outside source must be exactly equal to that given up by the gas during its expansion, in order to keep the temperature constant.
Similarly, during the isothermal compression of gas, heat must be removed from the gas in an amount equal to the heat energy of compression in order to maintain a constant temperature. Regardless of whether the compressor is air-cooled or water-cooled, the heat removed must be equal to the heat input done by the work of compressing the gas.
Tags:
Basics of Refrigeration