Material | Specific Heat CP CV | R | |
Air ................................... | 74 | .17 | 53.34 |
R-717 (Ammonia) . . . . | ,51 | .35 | 123.24 |
R-744 (Carbon Dioxide) | .22 | .17 | 38.82 |
Ether................................ | 48 | .45 | 23.11 |
Oxygen ........................... | 22 | .16 | 48.55 |
Alcohol ........................... | 45 | .40 | 41.55 |
Water Vapor ................... | 480 | .37 | 83.23 |
Fig. 1-23. A table of gas values (constants) for some
common substances.
common substances.
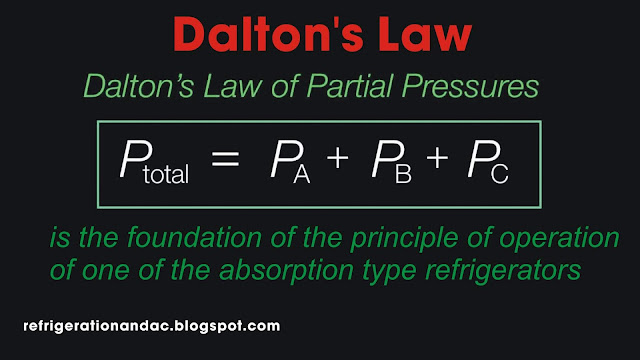
The total pressure of a confined mixture of gases is the sum of the partial pressures of each of the gases in the mixture." The total pressure of the air in a compressed air cylinder is the sum of the oxygen gas, the nitrogen gas, the carbon dioxide gas, and the water vapor pressure.
The law further explains that each gas behaves as if it occupies the space ALONE. This behavior also explains why water will evaporate from a floor after a scrubbing. The water vapor pressure is so low in the air that the water will turn to water vapor (very slowly of course) at temperatures of 70 F. down to freezing.
Tags:
Basics of Refrigeration