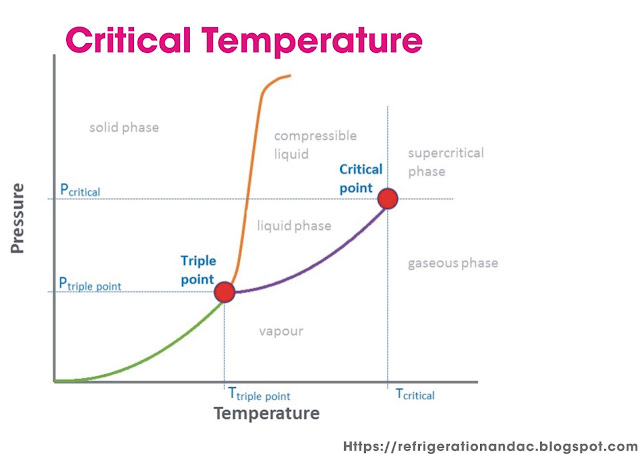
The critical temperature of a substance is the maximum temperature at which the substance may be liquefied, regardless of the pressure applied upon it. Refer to Chapter 27, for a list of critical temperatures for common refrigerants. The condensing temperature for all refrigerants must be kept below the critical temperature for the refrigerant used; otherwise, the refrigerator would not operate. Carbon dioxide (R-744) has a critical temperature of 87.8 F. This refrigerant cannot be used in air-cooled condensers because the condensing temperature would usually be above this temperature.
Tags:
Basics of Refrigeration